Inverter technology plays a crucial role in modern solar power systems. It converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity used by electrical appliances. Solar inverters are primarily categorized into three types: off-grid, grid-tied, and hybrid. Each type is suited to different needs and applications, making it essential to understand their characteristics before investing in a solar power system.
What is a Solar Inverter?
A solar inverter is a device that ensures a solar power system delivers usable electricity. It manages the flow of energy between the solar panels, energy storage batteries, and the power grid. Inverters are crucial for optimizing energy efficiency, ensuring compatibility with household appliances, and enabling advanced features like net metering. Without a reliable inverter, a solar power system cannot function effectively.
Types of Solar Inverters
1. On Grid Solar Inverter
On Grid Solar Inverter connect directly to the public power grid. They synchronize the solar system with the grid power and feed excess energy back into the grid.
Advantages
Grid-tied systems are cost-effective. They can reduce electricity bills and enable net metering, where users receive credits for the electricity they feed back into the grid. This option is ideal for urban areas with stable grid access.
Disadvantages
Grid-tied inverters cannot operate during power outages because they rely on the grid. This limitation makes them unsuitable for areas with frequent power interruptions.
2. Off-Grid Solar Inverters
Off-grid solar inverters operate independently of the power grid. They use batteries to store energy for later use.
Advantages
Off-grid systems provide energy independence and are ideal for remote areas, especially those without grid access. These inverters ensure a stable power supply even during power outages.
Disadvantages
Battery storage significantly increases costs. Since system capacity depends on battery capacity, users may need to carefully manage energy usage.
3. Hybrid Solar Inverters
Hybrid solar inverters combine the features of both grid-tied and off-grid systems. They can connect to the grid and manage battery storage.
Advantages
Hybrid systems offer flexibility. They ensure backup power during power outages and support net metering when the grid is available. Users can optimize energy use by storing excess energy or selling it back to the grid.
Disadvantages
Hybrid inverters have higher upfront costs due to their advanced features. Their installation process is also more complex compared to other types of inverters.
Grid-Tied, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Modes
Choosing the right solar inverter depends on factors such as cost, efficiency, installation, and intended use.
Cost
Grid-tied systems are the most affordable, while hybrid systems are the most expensive due to the integrated battery. Off-grid systems fall in between, depending on battery capacity.
Efficiency
Grid-tied systems are highly efficient in areas with stable grid access. Off-grid systems depend on battery quality, while hybrid systems offer a balance of efficiency and versatility.
Installation
Grid-tied systems are easier to install because they don't require batteries. Off-grid and hybrid systems require additional components, making installation more complex.
Use Cases
Grid-tied inverters are best suited for urban areas with stable power supply. Off-grid inverters are suitable for rural or remote areas without grid access. Hybrid inverters are ideal for users who need both flexibility and backup power.
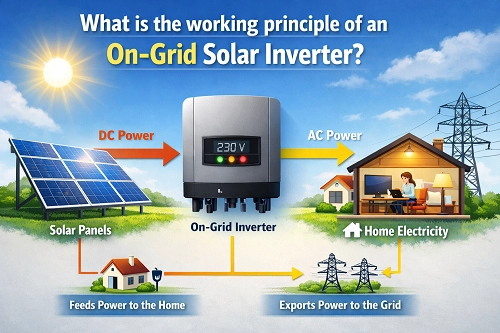
How do On Grid Solar Inverter work?
Solar energy, a clean and sustainable energy source, is rapidly gaining prominence. A key component of many solar energy systems is the grid-tied inverter. But what role does it play, and how does it work?
Converting DC to AC
The primary function of any solar inverter is simple: converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). Solar panels generate DC electricity when they absorb sunlight. However, our homes and most appliances within them use AC electricity. A grid-tied inverter bridges this gap, ensuring that the electricity generated by your solar panels can be used by your home.
Synchronizing with the Grid
Grid-tied inverters not only convert power but also synchronize it. The power grid operates at a specific frequency. The inverter ensures that the AC power it produces matches the frequency and voltage of the grid. This synchronization is crucial for safely and efficiently feeding excess power back into the grid.
Feeding Excess Power Back
One of the major advantages of a grid-tied system is the ability to send excess energy back to the grid. Let's say it's a sunny day, and your solar panels are generating more electricity than your home needs. The inverter doesn't waste this excess energy; instead, it sends it back to the main power grid. This process can earn you credits on your electricity bill, reducing your overall costs.
Drawing Power When Needed
Solar power generation is not constant; it varies with time and weather conditions. On cloudy days or at night, your solar panels may not generate enough power to meet your needs. In this case, the grid-tied inverter allows your home to draw power from the grid, ensuring uninterrupted power supply regardless of solar conditions.
Safety Features and Monitoring
A critical function of grid-tied inverters is safety. In the event of a power outage, the inverter automatically stops sending power to the grid. This feature, called anti-islanding protection, protects grid maintenance workers from unexpected power surges. Furthermore, many modern inverters come equipped with monitoring systems. These systems track power generation, consumption, and feedback, helping you understand and optimize your energy usage.
Maximizing Power Generation
Some grid-tied inverters feature Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). MPPT technology ensures that the inverter extracts as much power as possible from the solar panels, especially under less-than-ideal lighting conditions. It continuously adjusts to ensure optimal power conversion and efficiency.
What's the difference between grid-tied and off-grid solar inverters?
If you've been researching solar power solutions, you've probably come across the terms "grid-tied" and "off-grid" inverters. But what exactly do they mean? Let's explain in simple terms.
On Grid Solar Inverter
- Grid Connection: Grid-tied inverters connect your solar panels directly to the public electricity grid. This is their most significant feature.
- Net Metering: With this setup, any excess electricity your solar panels generate can be fed back into the grid. In many places, the utility company may pay you for this or provide a subsidy!
- No Energy Storage: One important point to note is that grid-tied systems typically don't have energy storage. If there's a power outage, your system won't work, even if it's sunny.
- Cost-Effective: Grid-tied inverters are generally cheaper than off-grid inverters. They don't require batteries, which saves a significant amount of money.
- Maintenance: These systems require less maintenance. No batteries mean no battery replacement or related maintenance.
Off-Grid Solar Inverters
- Independence is Key: The core of off-grid inverters is independence. They operate without being connected to the public electricity grid.
- Energy Storage is Crucial: To operate off-grid, these systems require batteries. The solar panels charge these batteries, and then your home draws energy from them.
- 24/7 Power (under certain conditions): As long as the batteries have power, you'll have continuous electricity. This is especially convenient during power outages. But remember, the stored energy is limited. If you run out, you'll need to wait for sunlight to recharge.
- Higher Initial Cost: Off-grid systems can have a higher initial cost. Batteries and related components add to the expense.
- Maintenance Considerations: Batteries don't last forever. Depending on the battery type and usage, you'll need to replace them every few years.
Which one is right for you?
- Assess Your Needs: Think about what you need. Do you need backup power during power outages? Or are you looking to reduce your electricity bills?
- Location Matters: If you're in a remote area without access to the grid, off-grid power might be a good option. Budget: Grid-tied systems may have lower initial costs, but off-grid systems provide power security.
Sunohoo Technology
Zhejiang Sunohoo Technology Co., Ltd, A Subsidiary Of Zhejiang Sunoren Solar Technology Co., Ltd. (Stock Code: 603105) Is Committed To Providing Green Energy Integrated With Smart Management Solutions So As To Improve The Economy And Reliability Of Users' Energy Usage.
Sunohoo Technology Is A Scientific And Technological Innovative Enterprise Of R&D, Design, Production And Sales To Provide Users With Excellent Energy Storage System Solutions. Currently We Have Off-Grid Photovoltaic Energy Storage Series,Hybrid Energy Storage Series, Portable Power Station Series , Etc. Sunohoo Technology Is Determined To Become A Forerunner And Demonstrator For Peak Carbon Dioxide Emission And Carbon Neutrality.
The choice between a grid-tied or off-grid inverter ultimately depends on your individual needs and circumstances. Grid-tied systems connect to the public power grid and are generally more economical and have lower maintenance costs. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, offer independence from the grid but require the added responsibility of battery maintenance.
Solar inverters are the cornerstone of renewable energy systems. Grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid inverters cater to different needs, making the selection of the right solution crucial. Companies like Sungrow lead the industry with innovative products that meet diverse energy requirements. By understanding the available options, you can make informed decisions to achieve your energy goals and contribute to a sustainable future.